The ABCs of Additive Manufacturing
A: About additive manufacturing
Additive manufacturing technology has definitely come a long way since the first commercial printer was invented by Charles Hull in 1984. More widely available now and at a lower cost, it has been quietly revolutionising its way across various industries – from manufacturing to healthcare, energy, defence and aviation.
Although commonly associated with toys and hobbyists (3D-printed Pokémon anyone?), additive manufacturing is incredibly useful for more than just simple modelling or prototyping. A few years ago, we wouldn’t have imagined that we could print actual human organs and yet, here we are.
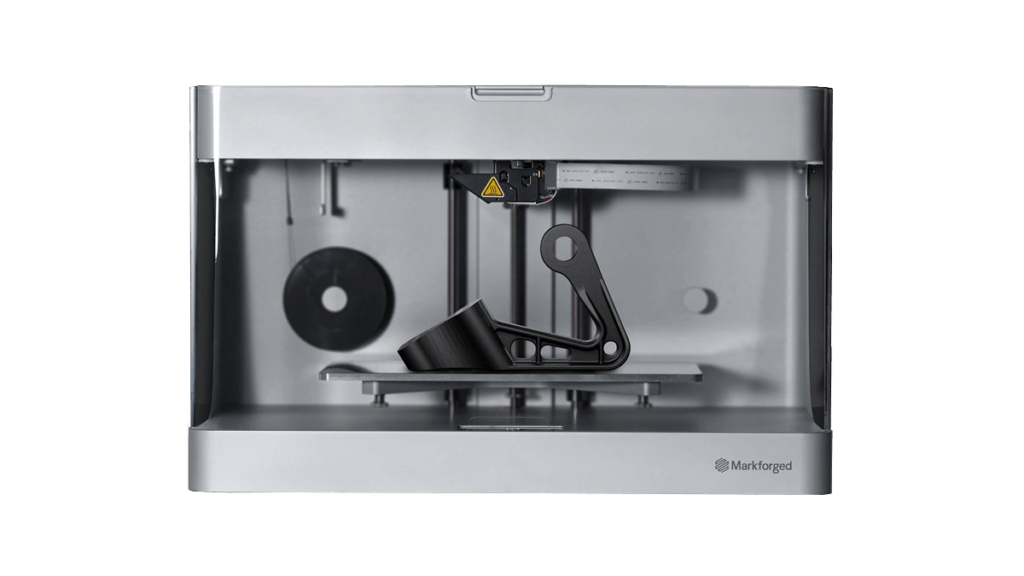

B: Benefits of additive manufacturing for us and our customers
Delphic has been in the precision tooling business for more than two decades but we’re always on the lookout for new and innovative ways to do things better and explore new manufacturing possibilities. For us, additive manufacturing was a logical progression with great benefits not just for our business but for our customers too.
More product options – additive manufacturing allows us to expand our product options. With 3D-printed molds, we can now provide low volume molding or casting.
Greater design flexibility – additive manufacturing also comes with fewer design restrictions, which means we now have the freedom to design complex geometries and develop creative yet practical solutions for our clients.
Shorter production time – One of the greatest advantages of additive manufacturing is a much faster production process. For instance, a design that takes us two weeks to produce using conventional methods could be completed overnight with a 3D printer.
Lower cost – In addition to saving time, opting for 3D-printed components could also potentially result in cost savings of 50% or more.

C: Composite materials and why it’s great for industrial applications like ours
After some careful research, we decided on Markforged 3D printers including the X7, Mark 2 and Onxy Pro, for their performance and sleek, compact exterior. It’s been an exciting few weeks as we dived into the world of composite 3D printing.
Why composite printing?
Industrial strength for industrial applications
For industrial applications like jigs, fixtures and other tooling, we need materials that are much, much stronger, more durable and stiffer than regular thermoplastics like ABS, nylon and PLA (which are typically used in most additive manufacturing processes). Composite materials like the ones we use are specially built for strength and have been proven to surpass thermoplastics in all these qualities.

Reinforced structure that enables the printing of strong, stiff and lightweight components
Unlike thermoplastics, composite parts are made up of more than one material and have a structure that comprise a matrix and a reinforcement, resulting in a strong, stiff and lightweight product. The matrix in Markforged composite material is onyx (a nylon-based thermoplastic mixed with chopped carbon fibre, and one of the best plastics for additive manufacturing) and the reinforcement is one of a few specific fibres.
Fibreglass – Engineering grade and affordable, fibreglass is 11 times more rigid than ABS and 3 times stronger with a flexural strength of 210 MPa and tensile strength of 590MPa. Ideal for tooling like drill jigs and soft jaws.
Carbon fibre – Extremely strong with a yield strength comparable to that of 6061 aluminium yet much more lightweight. 24 times more rigid than ABS and 60 times more rigid than nylon. Ideal for components that require maximum stiffness and minimal deflection.
Kevlar – Extremely durable and 15 to 20% lighter than the rest of the other fibre materials. Deflects without losing strength. Ideal for applications that involve a large amount of movement such as grippers.
High-strength high-temperature fibreglass (HSHT) – A unique Markforged material, HSHT retains strength even at temperatures above 150°C with an impact resistance 30 times stronger than ABS. Even at its maximum load, HSHT is able to deflect and return to its original dimensions once the load is lifted. Ideal for applications like welding fixtures, thermos forms, thermos set molds, injection mold inserts and blow molds.
Continuous filament fabrication (CFF) printing method
Unlike other types of additive manufacturing methods, Markforged printers use a signature CFF printing method, where the reinforcement fibres are printed continuously layer by layer. As a result, any weight, impact or load is then effectively distributed along the length of the fibre – firmly held in place by the matrix – and the printed part is made much stronger and much more rigid.
Delphic’s additive manufacturing process
Using 3D printing technology to produce top-quality precision tooling is a relatively simple process as we’ve tried to show in the diagram below.
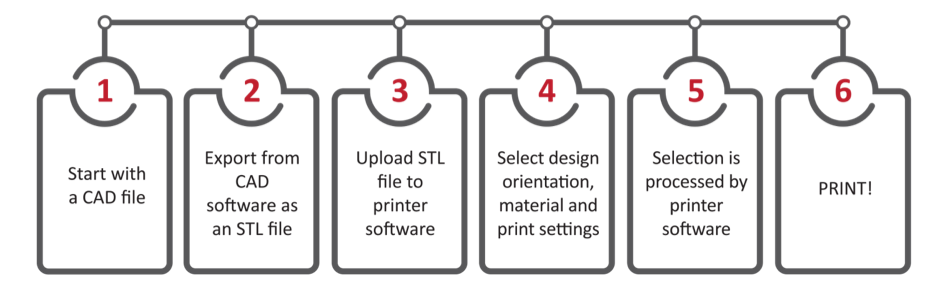
To date, having additive manufacturing capabilities has opened up a whole new world of opportunities for us. It allows us to develop new types of precision tooling and tooling applications as well as more creative and more complex designs that are not possible with conventional methods of production. Operationally, shorter production times means we can deliver the goods to you much more quickly than before.
For our customers, it requires adopting a different approach towards product design, understanding the fundamentals of additive manufacturing and learning how to harness its benefits to achieve the greatest results.
If you want to find out more about our additive manufacturing offerings, let us know !